Forged threaded tubes
Forged threaded tubes
1. Definition
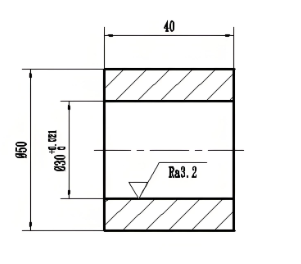
Forged threaded tubes are cylindrical components that have external or internal threads, produced through a forging process. They are used to connect pipes or other components in various applications, providing a secure and leak-proof connection.
2. Materials
These tubes are typically made from:
Carbon Steel: Commonly used for general applications due to its good strength and ductility.
Alloy Steel: Such as 4130 or 4140, which offers enhanced strength and toughness for more demanding environments.
Stainless Steel: For applications requiring corrosion resistance, such as AISI 304 or 316.
3. Manufacturing Process
Forging: The steel is heated to a malleable state and shaped under high pressure. This process enhances the mechanical properties and improves the grain structure.
Machining: After forging, the tubes may be machined to create precise threads and achieve specific dimensions.
Heat Treatment: Depending on the material and application, heat treatment processes (like quenching or tempering) may be applied to enhance hardness and durability.
4. Applications
Forged threaded tubes are commonly used in:
Piping Systems: For connecting pipes in oil and gas, water supply, and industrial applications.
Automotive: In components such as exhaust systems and oil lines where threaded connections are required.
Manufacturing: For securing parts in machinery and equipment.
5. Advantages
High Strength: Forged tubes exhibit superior strength and can handle significant loads and pressures.
Improved Integrity: The forging process results in fewer defects compared to cast components, ensuring a more reliable connection.
Corrosion Resistance: When made from stainless steel, these tubes provide excellent protection against rust and corrosion.
Versatility: Can be customized for various applications, ensuring compatibility with different systems and requirements.
Data Needed for Quotation
1) Your own drawing
2) Your requirement on material and necessary dimensional data
3) Ask for recommend
Processing Materials
| Case Hardened Comparison Table | |||||||
| GB | ГOCT | EN | DIN | W.N. | JIS | AISI/SAE | |
| 15CrMn | 16MnCr5 | 16MnCr5 | 1.7131 | 5115 | |||
| 20CrMn | 20MnCr5 | 20MnCr5 | 1.7147 | 5120 | |||
| 12CrMo | 12XM | 13CrMo44 | 1.7335 | 4119 | |||
| 15CrMo | 15XM | 15CrMo5 | 1.7262 | SCM415 | |||
| 20CrMo | 20XM | 20CrMo5 | 1.7264 | SCM420 | 4118 | ||
| 25CrMo | 30XM | 25CrMo4 | 1.7218 | ||||
| 30CrMo | SCM430 | 4130 | |||||
| 35CrMo | 35XM | 34CrMo4 | 1.722 | SCM435 | 4135 | ||
| 42CrMo | EN19 | 42CrMo4 | 1.7225 | SCM440 | 4140 | ||
| 50CrMo4 | 1.7228 | ||||||
| 40Cr | 40X | 41Cr4 | |||||
| 38XC | |||||||
| 25Cr2MoV | 25X2M1Φ | 24CrMoV55 | 1.7733 | ||||
| 50CrVA | 50CrV4 | 1.8159 | SUP10 | ||||
| 31CrMoV9 | 1.8519 | ||||||
| GCr15 | 100Cr6 | 100Cr6 | 1.3505 | 52100 | |||
| 20CrNiMo | 20XHM | 20NiCrMo2-2 | 21NiCrMo2 | 1.6523 | SNCM220 | 8620 | |
| 20XH3A | |||||||
| 20X2H4A | |||||||
| 17CrNiMo6 | 1.6587 | ||||||
| 18CrNiMo7-6 | 1.6587 | ||||||
| 34CrNiMo6 | 1.6582 | VCN150 | |||||
| 34NiCrMo16 | 35NiCrMo16 | 1.2766 | |||||
| 30CrNiMo8 | 1.658 | VCN200 | |||||
| 39NiCrMo3 | 1.651 | ||||||
| 34CrAlNi7 | 1.855 | ||||||
| 38CrMoAl | 38X2MОA | 41CrAlMo7 | 1.8509 | ||||
| 40CrNiMo | EN24 | 40NiCrMo8-4 | 1.6562 | SNCM439 | 4340 | ||
| 40CrNi | 40XH | 40NiCr6 | 1.5711 | ||||
| 20CrMnMo | 18XTM | SCM421 | |||||
| 40CrMnMo | 40XTM | SCM440 | |||||
| 30XTCA | |||||||
| 38XTH | |||||||
| 40XH2MA | |||||||
| 40X2H2MA | |||||||
| 38XH3MA | |||||||
| 38XH3MΦA | |||||||
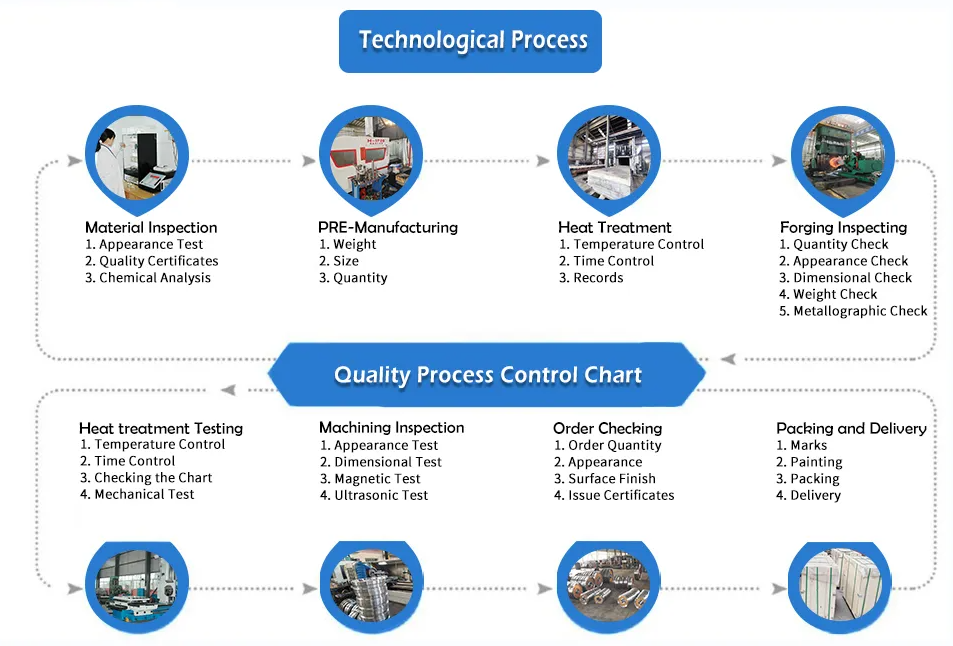
Processing technology:
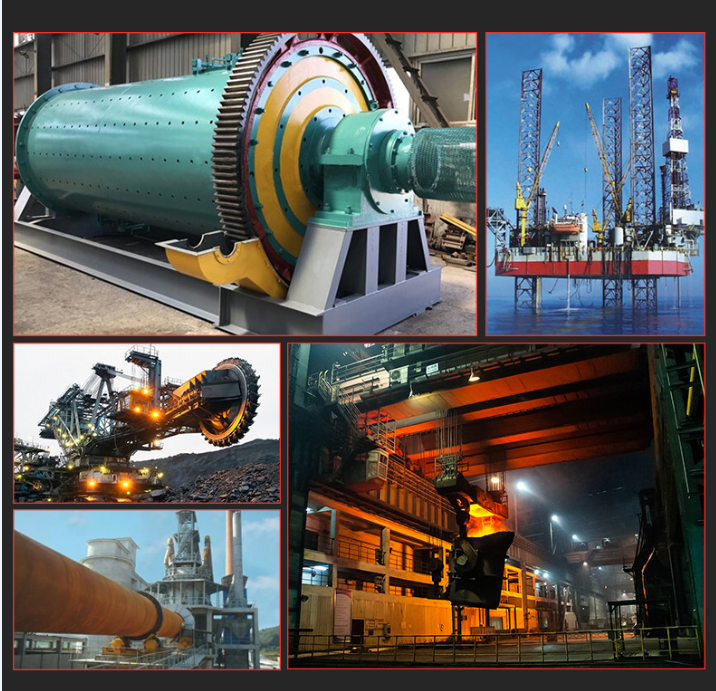
Application areas:
Automotive transmissions, medical equipment, metallurgical machinery, lifting equipment, ore equipment, power equipment, light industry equipment, etc

Packaging :




_1733312730.jpg)